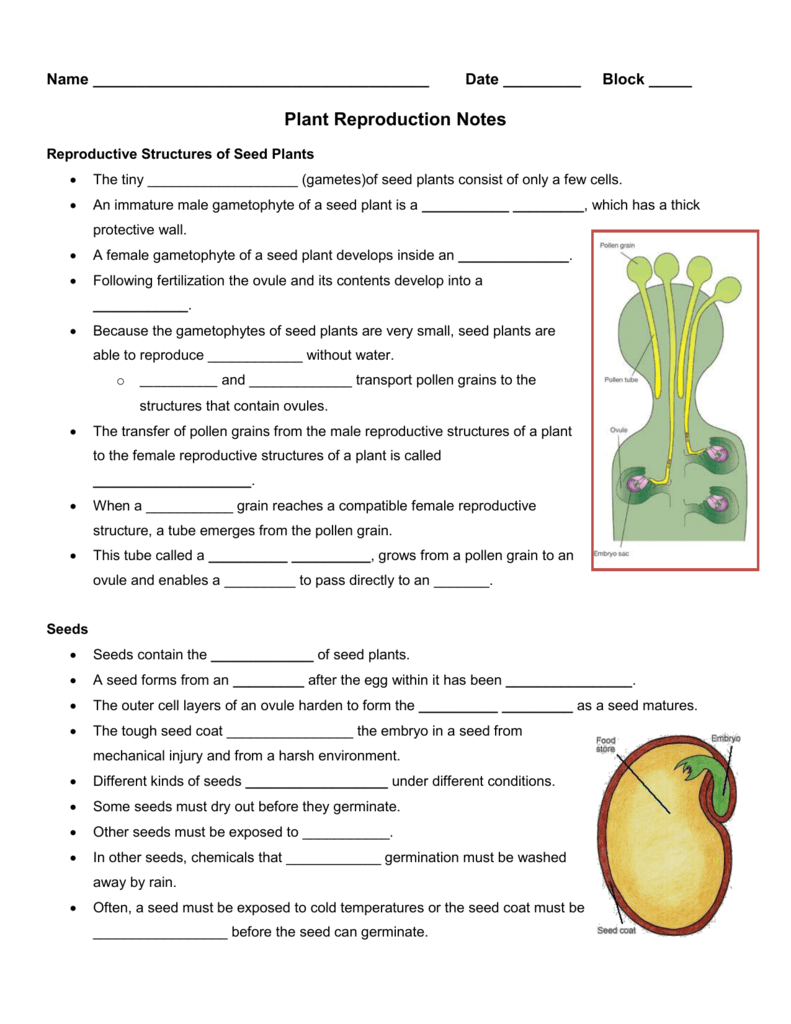
Pollen causes sneezing and runny noses, but it is also the crucial component in the sexual reproduction of plants and trees UNCTV Media Video BeeUtiful Bee Reporter's Blog Helping the Honey BeeAns The seed coat is the seed's hard outer covering It safeguards the internal organs of the tiny baby plant known as the embryo When we removeSeeds are also equipped to delay germination until growth conditions are optimal Pollen allows seed plants to reproduce in the absence of water The gametophytes of seed plants shrank, while the sporophytes became prominent structures and

How Do Seed Plants Grow Reproduce
Seed reproduction in plants
Seed reproduction in plants-Reproduction of seed plants answer key In sexual reproduction, the male and female organs produce male and female gametes, whose fusion results in a zygote After fertilization of the egg, the ovary becomes a seed and ovules become fruits Seed dispersal is necessary to separate the seed from the parent plant so that the seed can grow into aChapter 13 Sex and reproduction in nonseed plants Almost all plants are capable of reproduction without sex Most commonly this happens as a consequence of the plant being severed into pieces and these pieces being able to regenerate the parts that were lost Additionally, some species have developed pieces that are particularly prone to be




Plant Reproduction
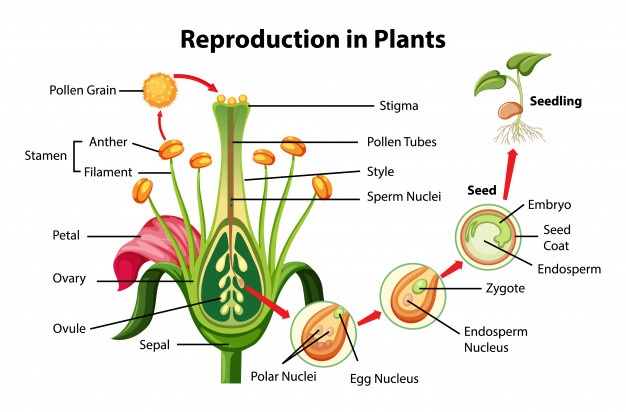
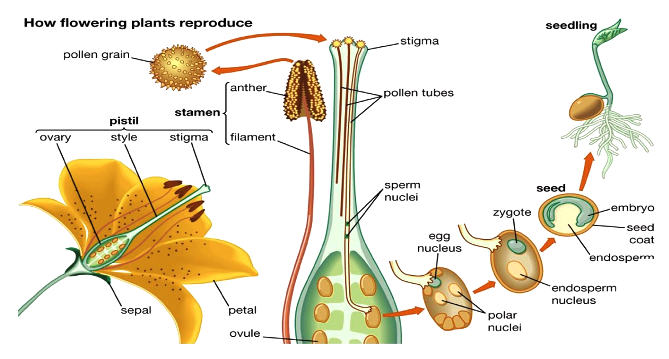
Q3 Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction Seeds are produced during sexual reproduction It Needs two parents Flowers help plants reproduce sexually A flower's most significant function is reproduction, so that it can produce seeds that can grow new plants Q4 State the main difference between asexual and sexual reproductionOnce pollen gets transferred to the stigma the male gametes from pollen grains release and fuse with the egg in the ovule to form a zygote This process of fusion of gametes is called fertilization The zygote thus formed, divides and develops into an embryo, and later into a seed The ovary develops into a fruitPLANT REPRODUCTION HOW TO CLASSIFY HUGUET FITÉ, Janet CEIP Antoni Roig Lesson 1 Name _____ Introduction How to classify Everyday, you classify Think about it Sorting objects and putting them in a specific place is classification NonSeed Plants Seed Plants Algae Mosses Ferns
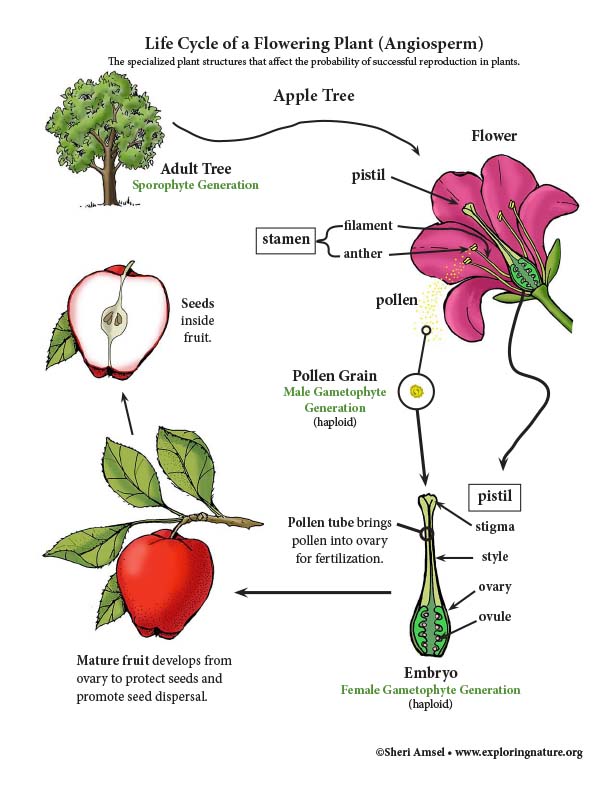
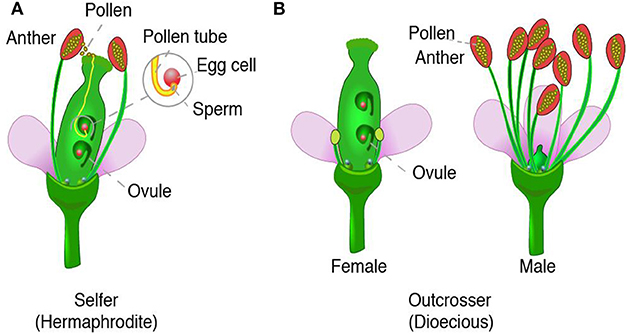
Flowering plants, also known as Angiospermae (/ ˌ æ n dʒ i oʊ ˈ s p ɜːr m iː /), meaning enclosed seeds in Greek, are the most diverse group of land plants with 64 orders, 416 families, approximately 13,000 known genera and 300,000 known species Like gymnosperms, angiosperms, which are also known by Magnoliophyta (/ m æ ɡ ˌ n oʊ l i ˈ ɒ f ɪ t ə,oʊ f aɪ t ə /), are seedEver wondered how seeds from one Plant get sown in a different area altogether? Modes Of Reproduction In Plants In plants, reproduction is carried out via two modes Asexual Mode – New plants are obtained without producing seeds;
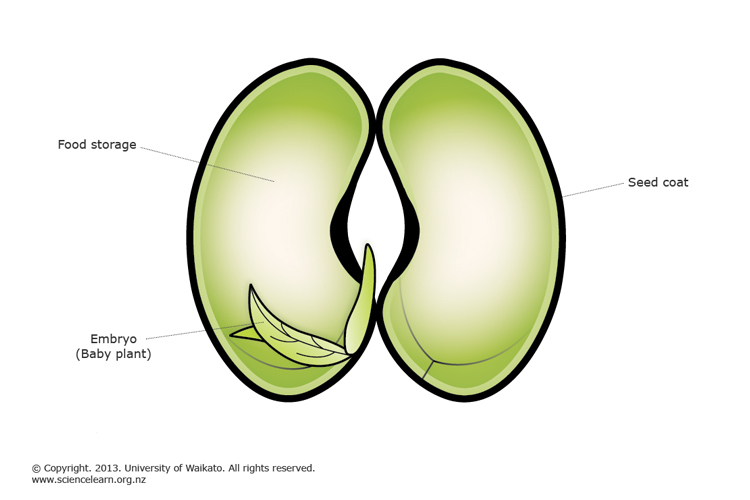
Reproduction is either sexual or asexual Sexual reproduction is the formation of offspring by the fusion of gametes Asexual reproduction is the formation of offspring without the fusion of gametes Sexual reproduction results in offspring genetically different from the parents Asexual offspring are genetically identical except for mutation In higher plants, offspring are packaged in a protective seed,Sexual and asexual Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes This results in genetically different offspring Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes These are genetically identical toSeed coat (testa) The seed coat is a tough, protective layer which prevents the embryo from being damaged and stops the entry of bacteria and fungi Embryo After fertilisation the zygote grows into an embryo The embryo develops two cotyledons (seed leaves), a plumule and a radilce Radicle will grow into the root during germination



Plant Reproduction Illustrated Growth And Development Of Organisms Ngss 6 8 Grade




Reproduction System Reproduction Systems In Plants Seed Propagated
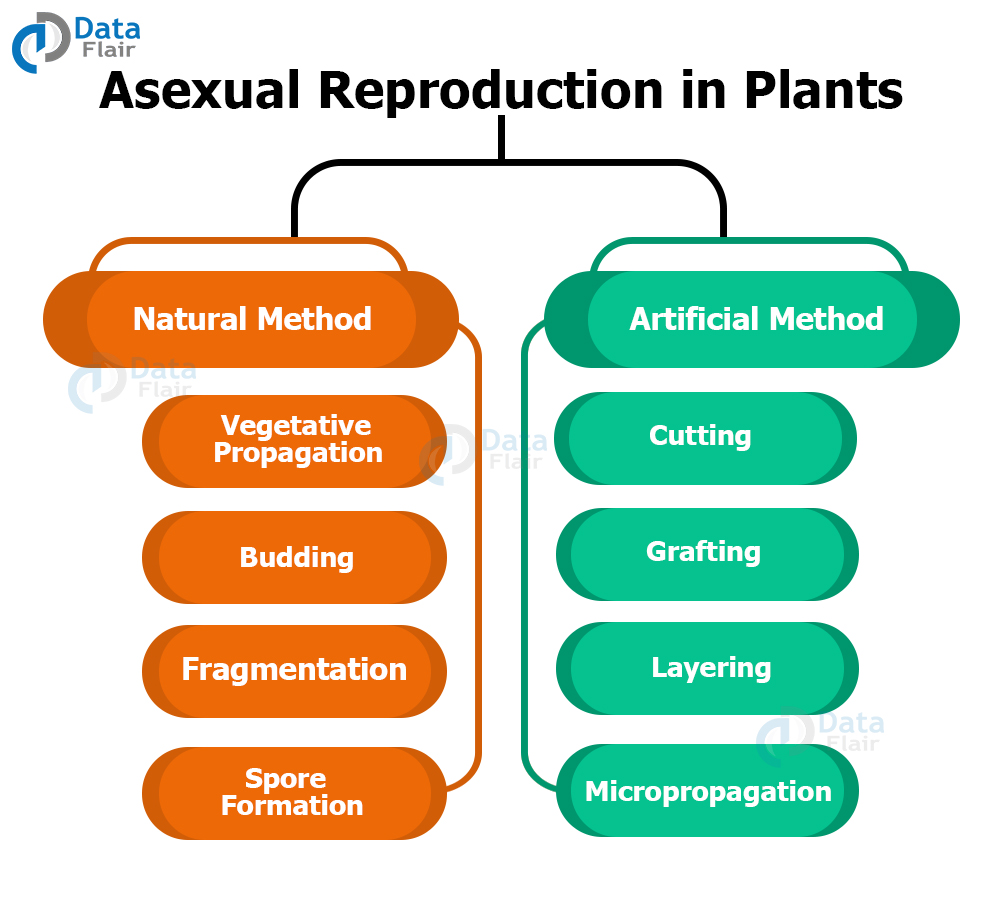
Plants have two ways of reproduction;Plant Reproduction Lesson Plan Printerfriendly version Send by email;Vegetative Reproduction Asexual reproduction is common in plants Vegetative reproduction leads to offspring that are identical to the parent The offspring develop by mitotic cell division of cells in stems, leaves, and roots Horticulturists use vegetative reproduction to propagate (grow) many identical plants




Lesson Worksheet Sexual Reproduction In Plants Nagwa



Plant Reproduction Notes Outline
Reproduction In Plants Plants can reproduce in different ways Flowering plants bear flowers They reproduce from seeds Some nonflowering plants reproduce from spores Plants can also reproduce from other plant parts Parts Of A Flower The petals of a flower are usually brightly coloured This attracts insects to come to it and help in the pollinationThe phenomenon of Seed Dispersal helps in reproduction in plants But what exAlthough plants can reproduce by other natural means, eg by seeds or by any of the abovementioned methods, man sometimes cuts the leaves or stems of plants and places them in either soil or water so that they can grow into new plants The new plants will have identical characteristics to their parent plants new plant develops from



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




How Do Seed Plants Grow Reproduce
32 Plant Reproduction Plant reproduction in plants can be accomplished via either sexual or asexual mechanisms Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parents Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically Asexual Reproduction Plants reproduce sexually through the fusion of male and female gametes in the flower Asexual reproduction is through stems, roots and leaves Plant reproduction comes in two types sexual and asexual Sexual reproduction is similar to human reproduction, in which male pollen and female ovarian germ cells fuse into a new The major difference between the methods is the existence of seeds The mode of reproduction decided the genetic structure of the plant Asexual reproduction produces new organisms without seeds while in sexual reproduction, seeds are mandatory This is



Outdoor Education School Science Camps California
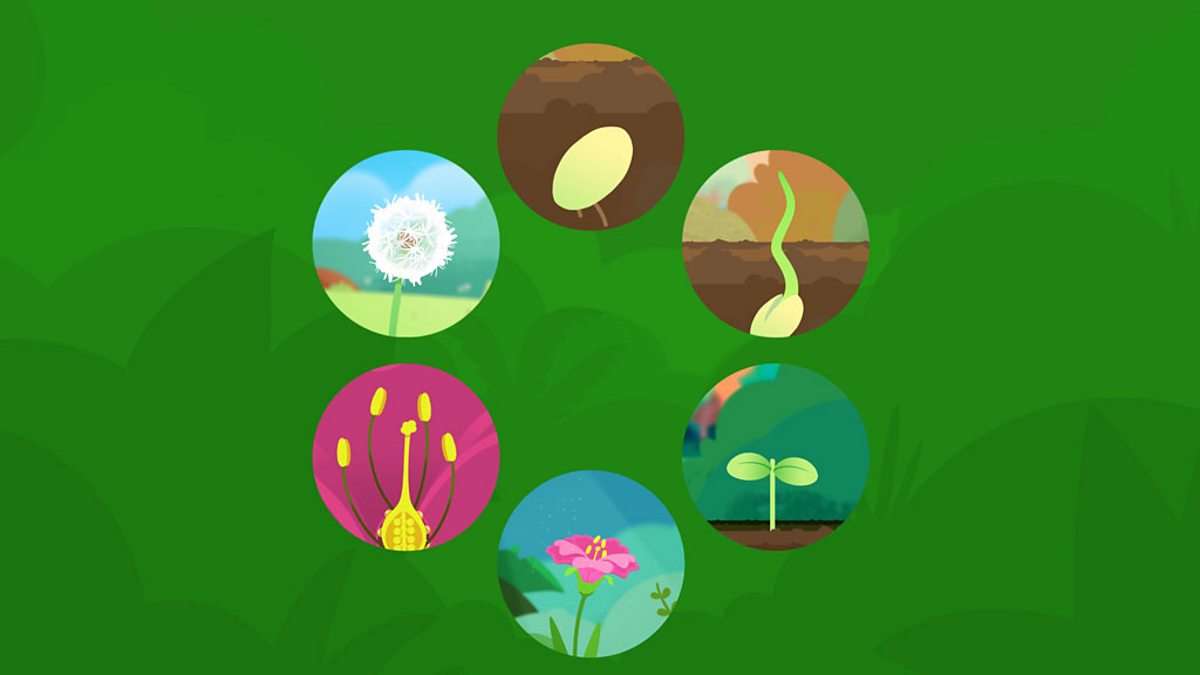




What Are The Stages Of A Plant S Life Cycle c Bitesize
In this video, we will be looking at sexual reproduction in plants Did you know that there are an estimated 390,900 plant species known to science?Sexual Mode – New plants are obtained from seeds Asexual Reproduction In Plants In asexual reproduction in plants, plants are reproduced without the formation of seeds Following are a few ways in which plantsFinally, using plants that Xowered or became vegetative in 04 all Xowers in the experiment (ie including those with Spearman rank correlations were calculated between no seeds), we calculated the seed/ovule ratio for each seed numbers in 05 and plant size in 05, and then 123 Oecologia (07) –524 519 between seed numbers in




Plant Reproduction Seed Plants




Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub
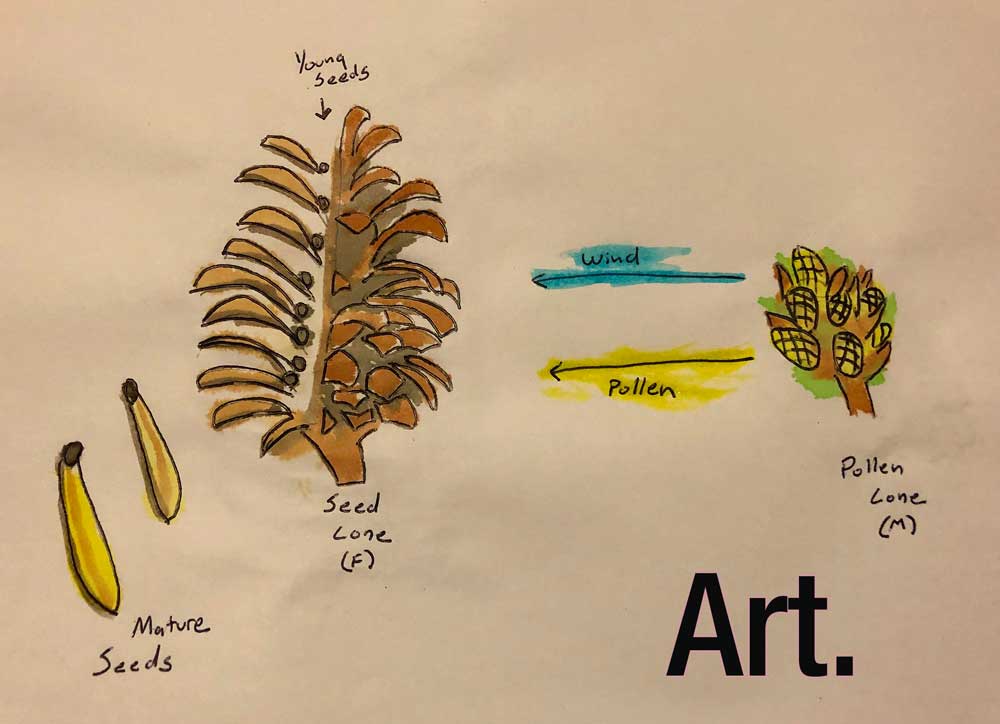
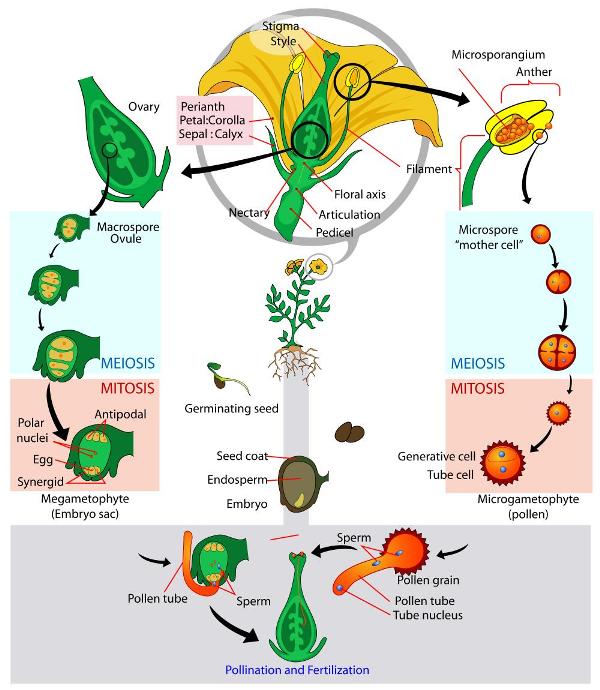
seed, the characteristic reproductive body of both angiosperms (flowering plants) and gymnosperms (eg, conifers, cycads, and ginkgos ) Essentially, a seed consists of a miniature undeveloped plant (the embryo), which, alone or in the company of stored food for its early development after germination, is surrounded by a protective coat (the testa)Both gymnosperms — plants with cones — and angiosperms — plants with flowers — carry out sexual reproduction, but angiosperms use flowers to hold developing seeds Pollen is the "male" cell that fertilizes a plant's egg cell In a gymnosperm, pollen reaches the egg when wind blows the pollen onto a female coneSome plants can produce seeds without fertilization Either the ovule or part of the ovary, which is diploid in nature, gives rise to a new seed This method of reproduction is known as apomixis An advantage of asexual reproduction is that the resulting plant will reach maturity faster




Seed Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help



How Seep Plants Reproduce Study Sheet Hanford Christian School Jane Kitson
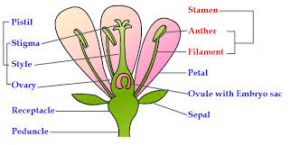
Sexual reproduction reproduction that involves fusion of 2 gametes Natural vegetative propagation in flowering plants involves the growth of a new part of a plant (bud/stem), which eventually becomes separated from the parent plant to form a new individualMethods of reproduction in flowering plants Describe that in asexual reproduction all the inherites traits come from a single parent ACONTENT Explain how one plant uses both sexual and asexual reproduction Name some of the asexual methods of plant reproduction and explain them Language OF learning Key phrases nedeed Sexual reproduction in plants To reproduce sexually plants have male and female reproductive organs in their flowers The male part is called the stamen The female part is called the carpel 7 POLLINATION It is the transfer of pollen grains from the anthers to the stigma Pollinating agents Insects Wind 8



Reproduction In Plants Psle Science




Plant Reproduction Seed Plants
The zygote will start to divide and eventually form a seed within the ovule;Plant Reproduction Topic Notes 3 Dormancy is a resting period for the seed when it undergoes no growth It allows the plant to avoid harsh winter conditions and maximises the survival of plants from each seed Germination is the regrowth of a plant embryo after a period of dormancy, when environmental conditions are suitable( the embryo must be alive, factors maintaining dormancy Answer Seed leaves or cotyledons provide food for the baby plant before green leaves emerge Long questions and answers of class 5 reproduction in plants What are the various parts of a seed?



What Is Reproduction In Plants Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki



Asexual Sexual Reproduction In Plants Pollination Stages Of Fertilization Process In Plants Science Online
Modes Of Reproduction in Plants There are several ways by which plants produce their offspring These are categorised into two types (i) asexual, and (ii) sexual In asexual reproduction plants can give rise to new plants without seeds, whereas in sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seeds All plants have the means and corresponding structures for reproducing sexually The basic function of a flower is to produce seeds through sexual reproduction Seeds are the next generation, serving as the primary method in most plants by which individuals of the species are dispersed across the landscapeAs different plants have different numbers of ovules, this explains why different fruits (which develop from the ovary) have different numbers of seeds (which develop from the ovules) Growth of a pollen tube Fertilisation in a flowering plant



Reproduction In Plants Sexual Reproduction And Asexual Reproduction Dataflair




Lesson Worksheet Sexual Reproduction In Plants Nagwa
Spider Plant Reproduction Spider plants have dark green or variegated leaves that are long and come to a point After the spider plant becomes root bound in the pot, reproduction starts and the spider plant has babies Flowers Spider plants produce long runners that sprout off of the mother plantSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plant class 12 biology All important terms #biology NCERT Reproduction in flowering plants begins with the process of pollination during which the male gametes are transferred to the female ovules Following pollination, fertilization involves the growth of the pollinated ovules into seeds As the seeds develop within the fruit of the flower, the fruit ripens and the seeds are freed from the fruit to




The Plants The Bees Plant Reproduction Video Khan Academy




Science Plant Reproduction Without Seed English Youtube
Plant reproduction without seeds Not every plant grows from a seed Some plants, like ferns and mosses, grow from spores Other plants use asexual vegetative reproduction and grow new plants from rhizomes or tubers We can also use techniques like grafting or take cuttings to make new plantsThree methods of plant asexual reproduction are Bulbs underground food storage organs with fleshy leaves that store food and can grow and develop into new plants, eg onions and garlicA couple of weeks ago I talked about a strategy for reproduction that the very first plants came up with called alternation of generation the strategy that nonvascular plants still use today hopefully this is coming back to you a plant can take two different forms that alternate back and forth between generations the first form the sporophyte has diploid cells two sets of chromosomes in




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica




Fun Germination Facts For Kids
The reproduction by vegetative propagation occurs only in plants Vegetative propagation usually involves the growth and development of one (or more) buds present on the old part of the plant to form a new plantRoots, stem, and leaves, plus a bit of stored food to help the plant begin to grow Seeds germinateonly in the right conditions Soil temperature, the amount of daylight or darkness, oxygen levels, and water availability all play a role in germination for various seeds Seeds produced through fertilization contain genetic material from both parents As a result, the offspring are not genetically identical to either of the parent plants This genetic diversity can help them survive if the environment changes Flowering plants reproduce sexually through a process called pollination



Plant Reproduction Comic Science With The Amoeba Sisters




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow
Plant Reproduction and Classification A reproductive cycle in which a gamete producing or gametophyte (n) alternates with a 2n zygote, 2n multicellular, or 2n sporophyte phase In plants, it is a reproductive cycle in which a haploid, diploid, or polyploid (n) phase (the gametophyte phase, which is multicellular plants) produces gametesPlant reproductive system, any of the systems, sexual or asexual, by which plants reproduce Asexual reproduction results in offspring that are identical to the parent plant Sexual reproduction involves new genetic combinations and results in offspring that are genetically different from the parent plantsPlant reproduction worksheets and online activities Free interactive exercises to practice online or download as pdf to print



Learn About Flowering Plant Reproduction Chegg Com



B2 Sexual Reproduction In Plants Lydia G Narain




Outdoor Education School Science Camps California




Illustration Biology Pollination Plant Flowering Plant Stock Vector Royalty Free




3d Flower Model Plant Science In 21 Flower Reproduction Plant Science Diagram Of A Flower




Chapter 24 Reproduction Of Seed Plants Ppt Video Online Download




13 3 Sexual Reproduction In Seed Plants



Sexual Reproduction In Plants



Biology For Kids Flowering Plants




Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants S Cool The Revision Website




Quotes About Plant Reproduction 23 Quotes




Reproduction In Plants




Seed Plants What Is The Difference Between A Seed Plant And Any Other Plant What Do Seeds Do How Do Plants Reproduce If They Don T Use Seeds Ppt Download



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds



1



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Characteristics Advantages Disadvantages




Plant Reproduction Bioninja
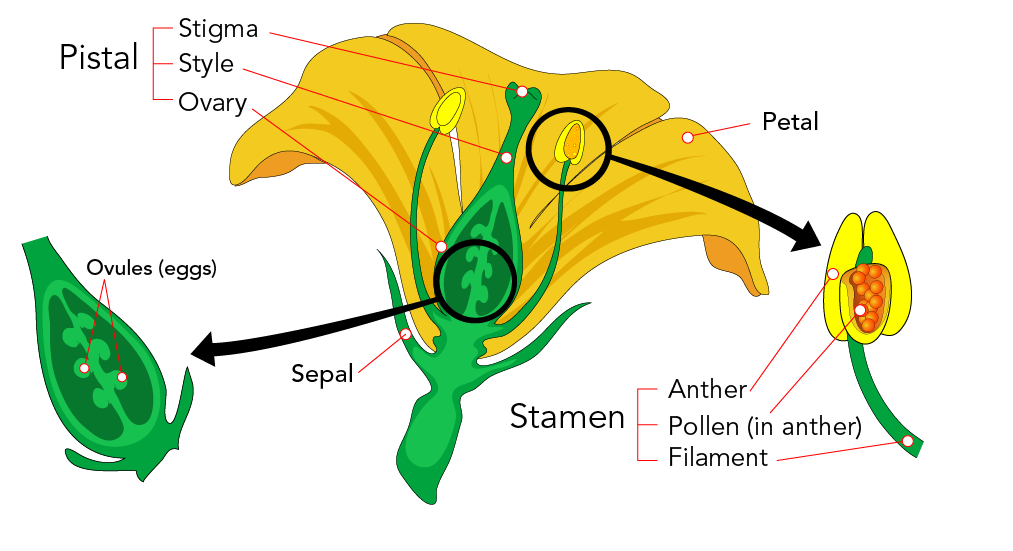



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Stamen Definition Description Facts Britannica




Dk Science Seed Plants
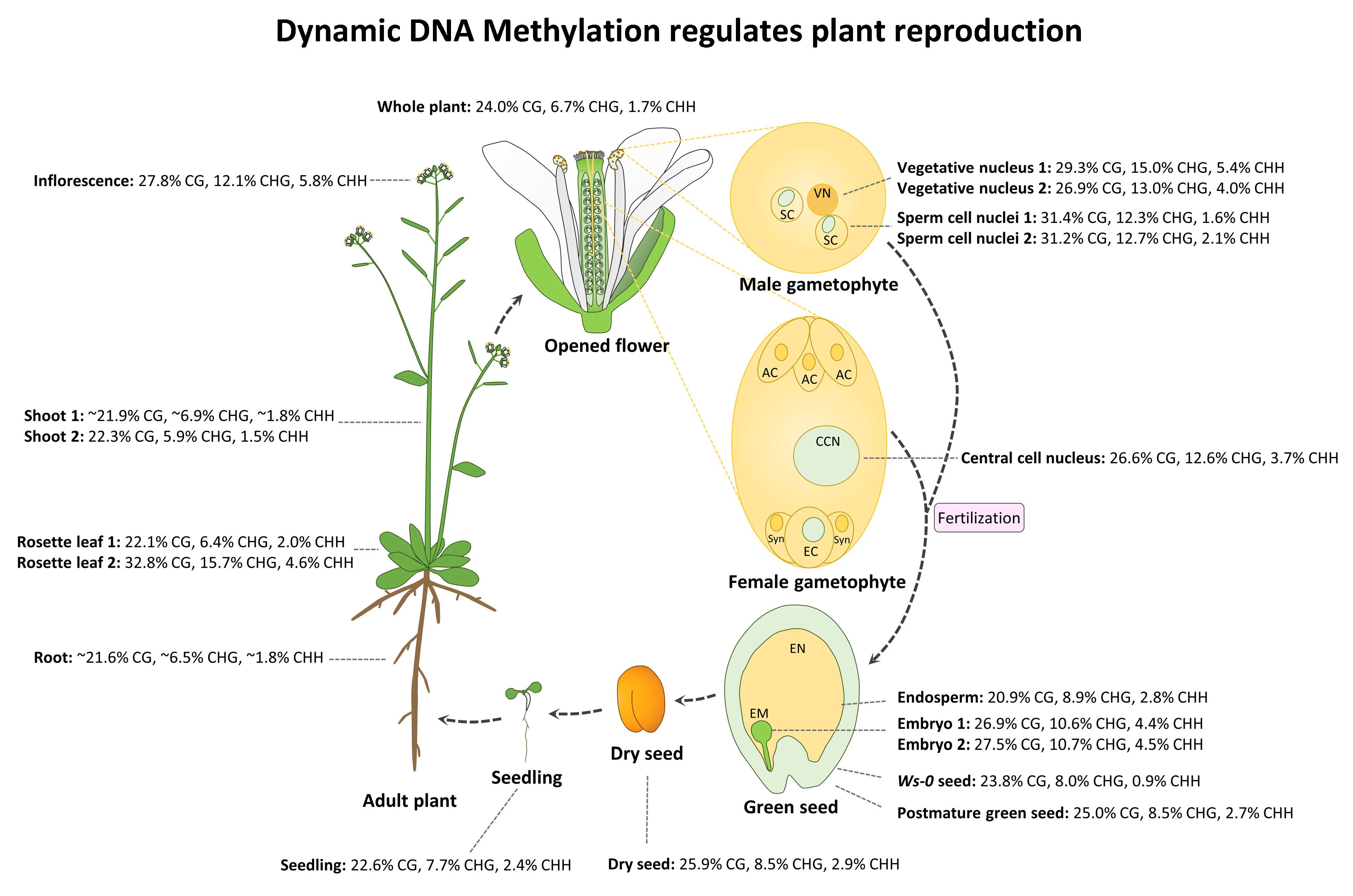



Plants Free Full Text Epigenetics Regulates Reproductive Development In Plants



1



How Do Plants Reproduce Sexually B4fa




Plant Reproduction Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
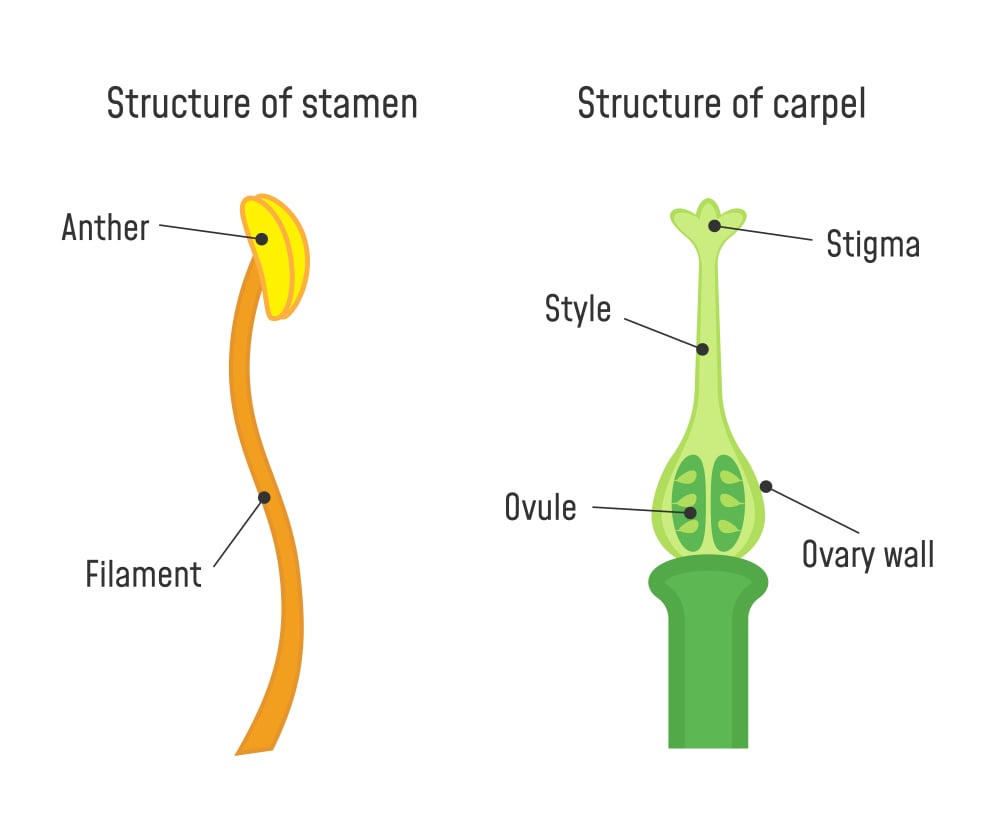



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce




Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download
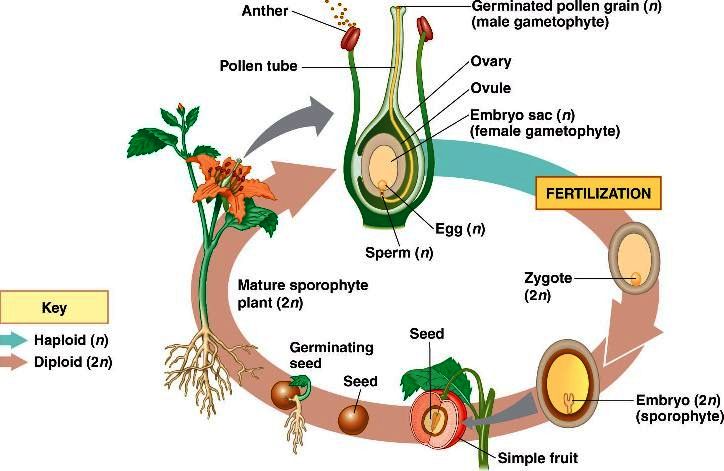



The Stages Of Fertilization Process In The Plants Science Online




Plant Nutrition And Reproduction Worksheet
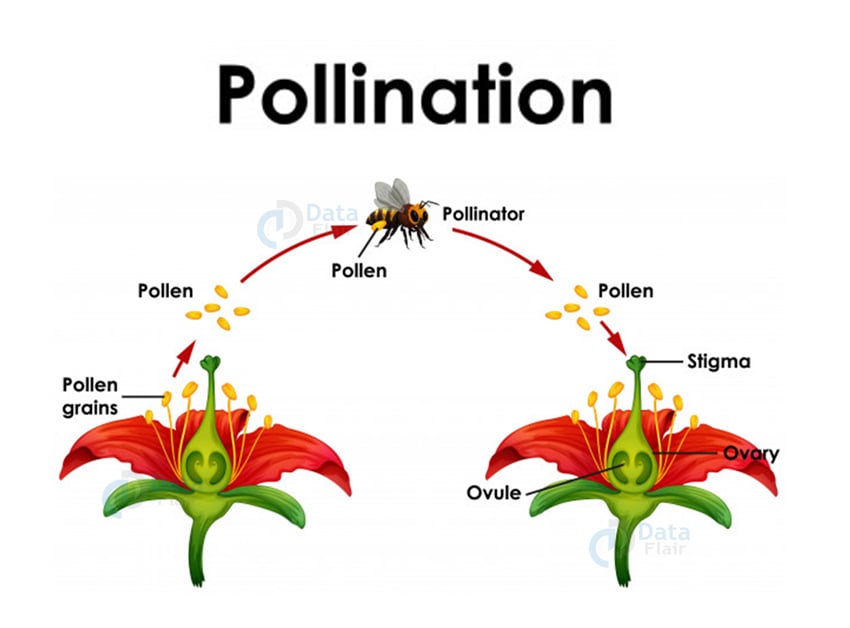



Reproduction In Plants Sexual Reproduction And Asexual Reproduction Dataflair




Reproduction In Flowering Plants Operation Plant



Asexual Reproduction Biology Ii




Seeds Of Flowering Plants Advanced Ck 12 Foundation



Tomatosphere Tomatosphere The Life Cycle Of A Tomato Plant




Learn Characteristics Of Living Organisms Nutrition Growth Reproduction And Lifespan In 3 Minutes




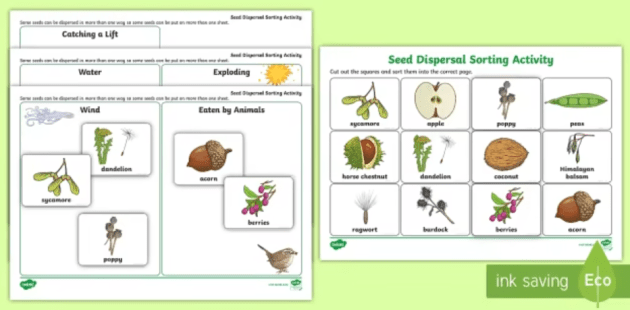
Seed Dispersal Interactive Worksheet



3




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow




Plant Reproduction



Lessons Blendspace




Learnhive Cbse Grade 5 Science Reproduction In Plants Lessons Exercises And Practice Tests




5 Reproduction Of Plants How Do Plants Reproduce




Types Of Reproduction In Plants Youtube




School Learning Zone Plant Life Cycles




Seed Plant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
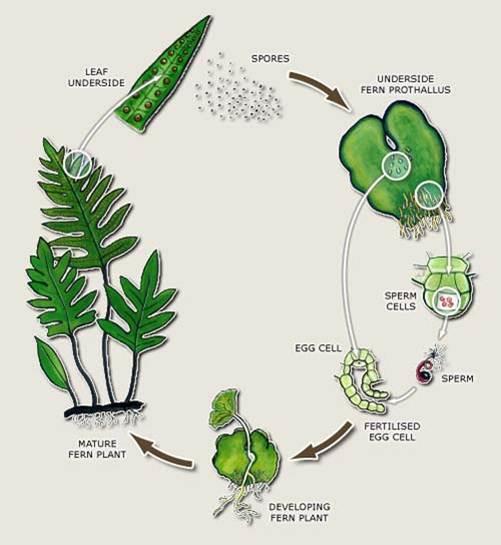



Seeds Vs Seedless Plants Biology Socratic




Mcq On Plant Reproduction By Biology Experts Notes Medium




On The Trails From Spores To Seeds Juneau Empire



Flowering Plant Reproduction




Reproduction In Plants 5th Std Science Cbse Board Home Revise Youtube




Science Plant Reproduction Year 5 What Trees Have




Forestry Learning Seeds Growth And Develop




Plant Reproduction Plant Reproduction What Are The Basic




Plant Reproduction Plants




Plant Fertilization Process Definition Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Reproduction Different Modes Of Plant Reproduction Byju S
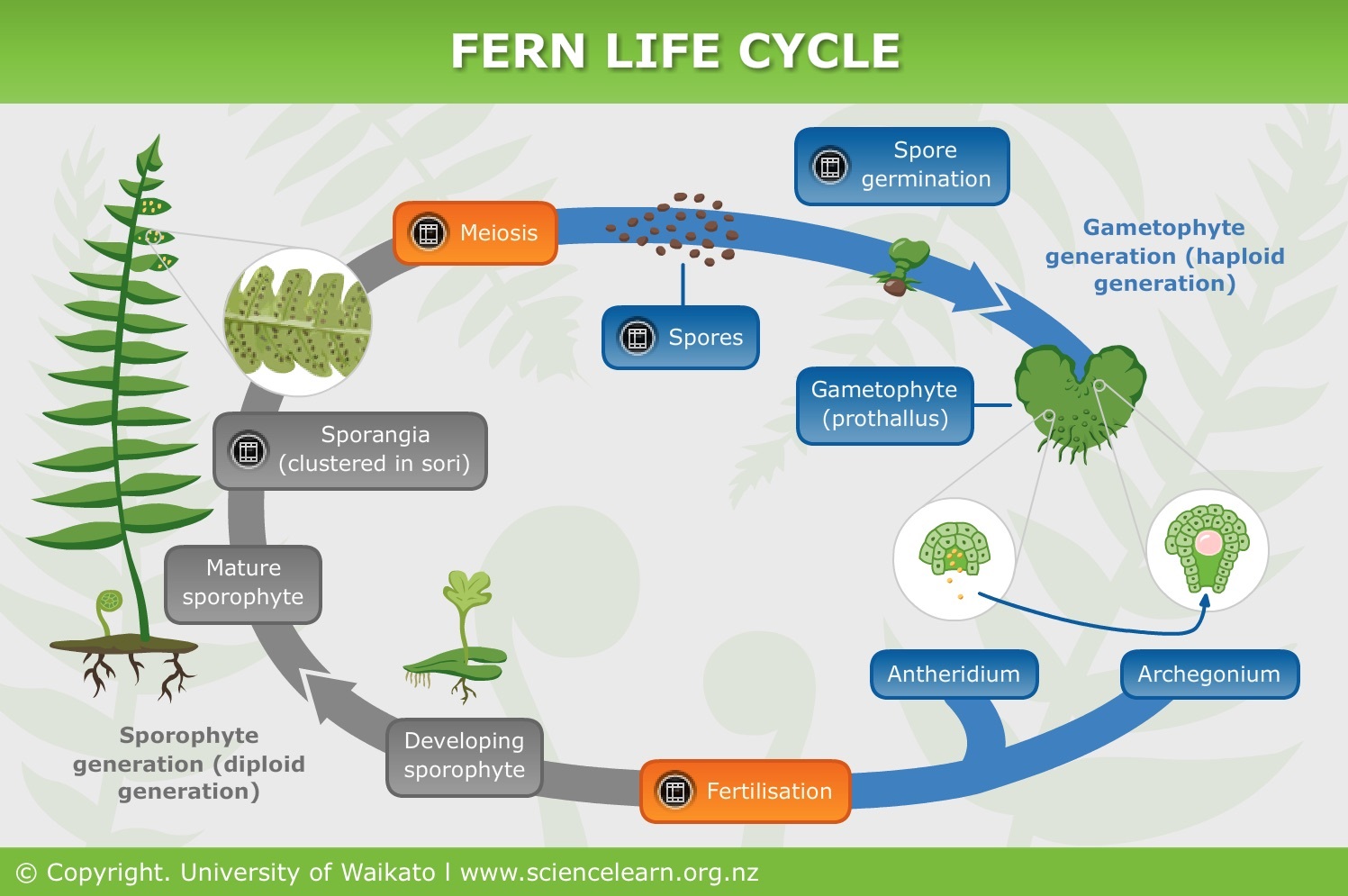



Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub



Reproduction In Plants




Plant Reproduction Sexual And Asexual Vegatitive Propogation Flashcards Quizlet



Seeds




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii




Plant Growth And Reproduction 4th Grade Science Nebraska Core Academic Content Standards




Why Are Seeds So Important Worldatlas
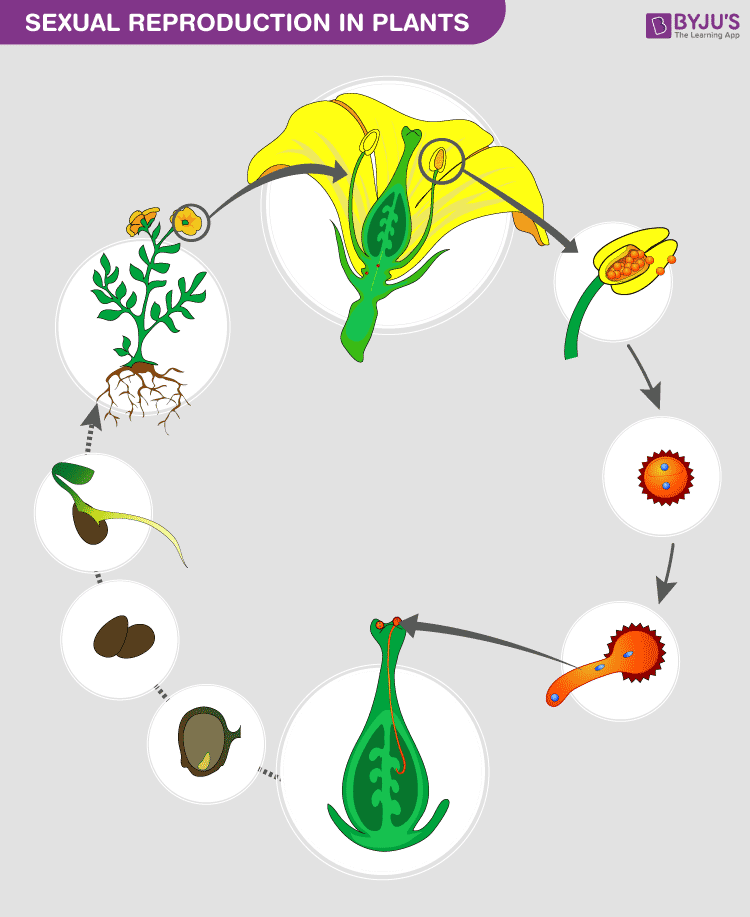



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Features And Its Process




Vegetative Propagation In Plants Definition Methods Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Yr 9 Topic 7 Reproduction In Plants Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
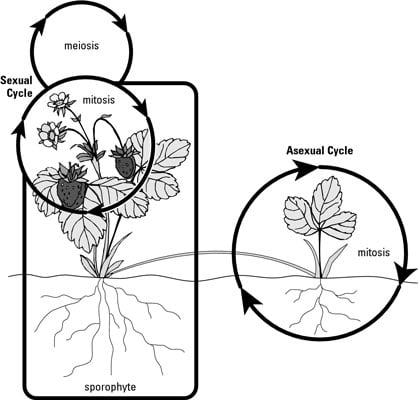



Plant Reproduction Dummies




4 Germination Sexual Reproduction In Plants
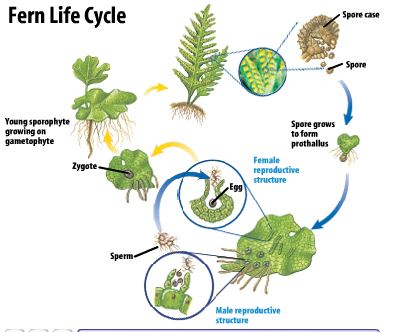



Sexual Reproduction Grade 11 University Biology
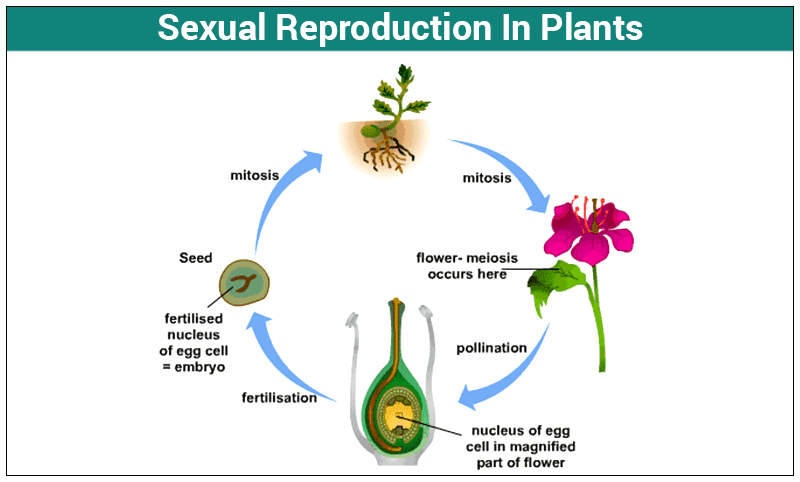



How Do Organisms Reproduce Tutormate



What Does The Process Of Pollination Involve Quora
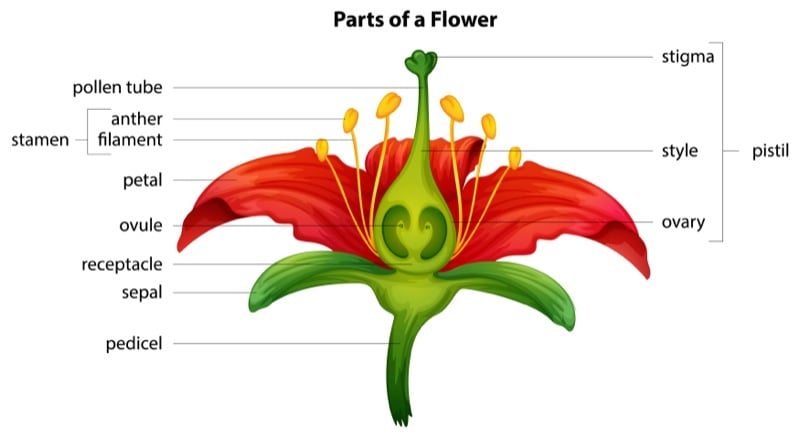



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce




Plant Reproductive Development And Structure Boundless Biology




Plant Reproduction Wikipedia
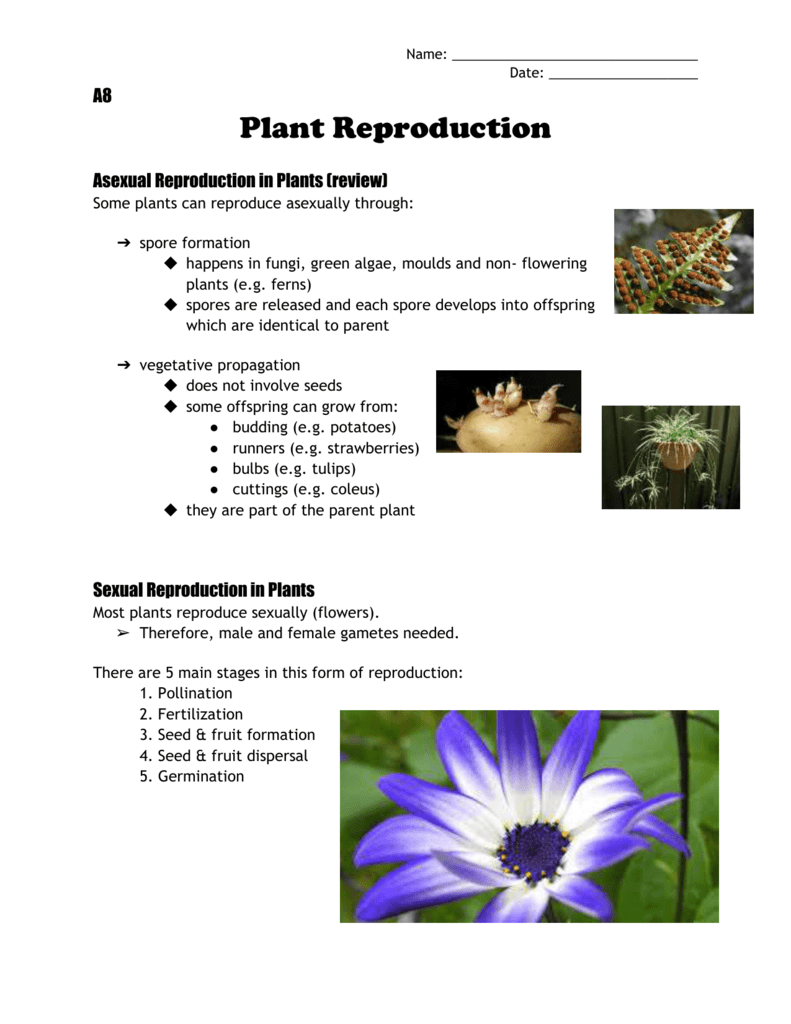



12 Plant Reproduction
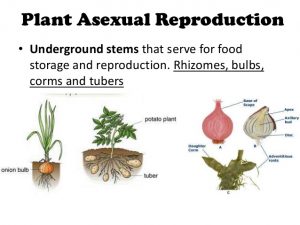



Advantages And Disadvantages Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants Science Online




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express
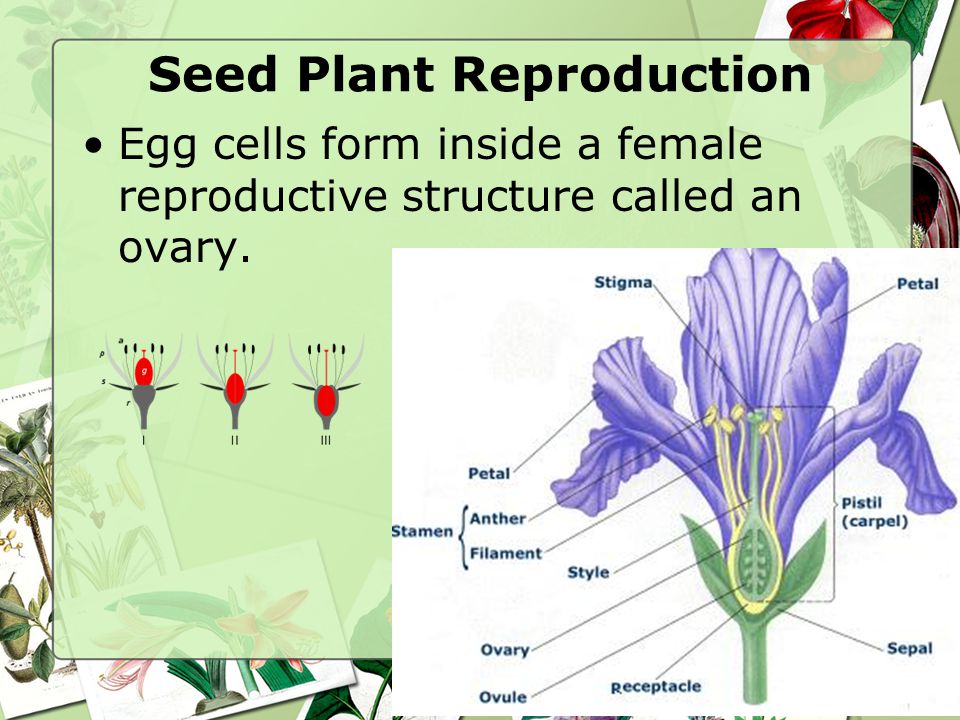



3 2 Notes Plant Reproduction Ppt Download




Reproduction In Plants Class 5 Youtube



Flowering Plant Reproduction




Plant Reproduction Powerpoint Presentation Lesson Plan Powerpoint Lesson Plans Powerpoint Lesson Alternation Of Generations



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿